Better Lawns and Gutters
Many of these practices can earn you Stormwater Utility Fee credits and incentives.
 Rain Barrel: Structures designed to intercept and store rain runoff from rooftops for a beneficial re-use. Typically, a rain barrel is a 55-gallon container connected to a downspout that can be re-used for irrigating the garden. Rain Barrels reduce potable water usage. Always irrigate before 10am and after 5pm as much irrigation water will evaporate away during the middle of the day. More Info
Rain Barrel: Structures designed to intercept and store rain runoff from rooftops for a beneficial re-use. Typically, a rain barrel is a 55-gallon container connected to a downspout that can be re-used for irrigating the garden. Rain Barrels reduce potable water usage. Always irrigate before 10am and after 5pm as much irrigation water will evaporate away during the middle of the day. More Info
 Rain Garden: A planted, shallow depression in the ground that allows stormwater to be absorbed. Rain gardens provide stormwater storage, reduce runoff, and filter and absorb pollutants to improve water quality. More Info
Rain Garden: A planted, shallow depression in the ground that allows stormwater to be absorbed. Rain gardens provide stormwater storage, reduce runoff, and filter and absorb pollutants to improve water quality. More Info
 Permeable Paving: A range of sustainable materials and techniques for pavements that have a base and subbase that allow the movement of stormwater through the surface. In addition to reducing runoff, permeable pavements effectively trap suspended solids and filter pollutants from the percolated water. More Info
Permeable Paving: A range of sustainable materials and techniques for pavements that have a base and subbase that allow the movement of stormwater through the surface. In addition to reducing runoff, permeable pavements effectively trap suspended solids and filter pollutants from the percolated water. More Info
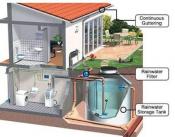 Cistern: An underground reservoir or tank for capturing and storing rain water. The stored, non-potable water is primarily used for irrigation. More Info
Cistern: An underground reservoir or tank for capturing and storing rain water. The stored, non-potable water is primarily used for irrigation. More Info
Green Roof: A roof of a building that is completely or partially covered with vegetation and a growing medium, planted over a waterproof membrane. Green roofs absorb rainwater, provide insulation, and help lower urban air temperature. They reduce runoff, and filter and absorb pollutants in stormwater to improve water quality. More Info
Wet Detention Basin: Stormwater detention basin constructed to replenish the natural wetland treatment process and provides storage and reduced runoff. They also filter and absorb pollutants to improve water quality. Wetland detention basins also provide habitat for local species and food.
More Info
Integrated Pest Management: A comprehensive approach of controlling insects, weeds, and plant pathogens with environmentally and economically sound practices. Integrated pest management reduces the chemicals applied to gardens and lawns that will wash off during storms and pollute local streams and creeks.
More Info
Fertilizing: Fertilizer influences your lawn's color, ability to recover from stress, and helps prevent weed invasions. Organic fertilizers are derived from plant or animal sources and add nutrients, structure, and retain moisture. Excessive fertilizing especially before it rains can wash into surface waters damaging the ecology. Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are the three major nutrients needed by lawns, although many lawns need little or no phosphorus.
More Info
Composting: Composting is the biological decomposition of organic material into a humus-like substance that can be used as a landscape fertilizer. Composting food scraps and landscape trimmings will reduce landfill waste.
More Info
Native/Drought tolerant/Pollinator Supportive Plants: Pollinators need plants that provide pollen and nectar throughout the growing season for species like honeybees as well as those that complete their nesting cycle in the spring or fall. The plants in these model plots collectively bloom through the seasons.
More Info
Stormwater Credits and Incentives: Reduce your stormwater utility fee or get a rebate for some better lawns and gutters activities. More Info
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| 827.1 KB |
